Nanotherapeutics of phytoconstituents for parasitic diseases: a short review
Nanotherapeutics of phytoconstituents for parasitic diseases: a short review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54117/gjpas.v1i1.2Keywords:
Nanotherapeutics, Phytoantioxidants, Parasite, Secondary Metabolites, NanodeliveryAbstract
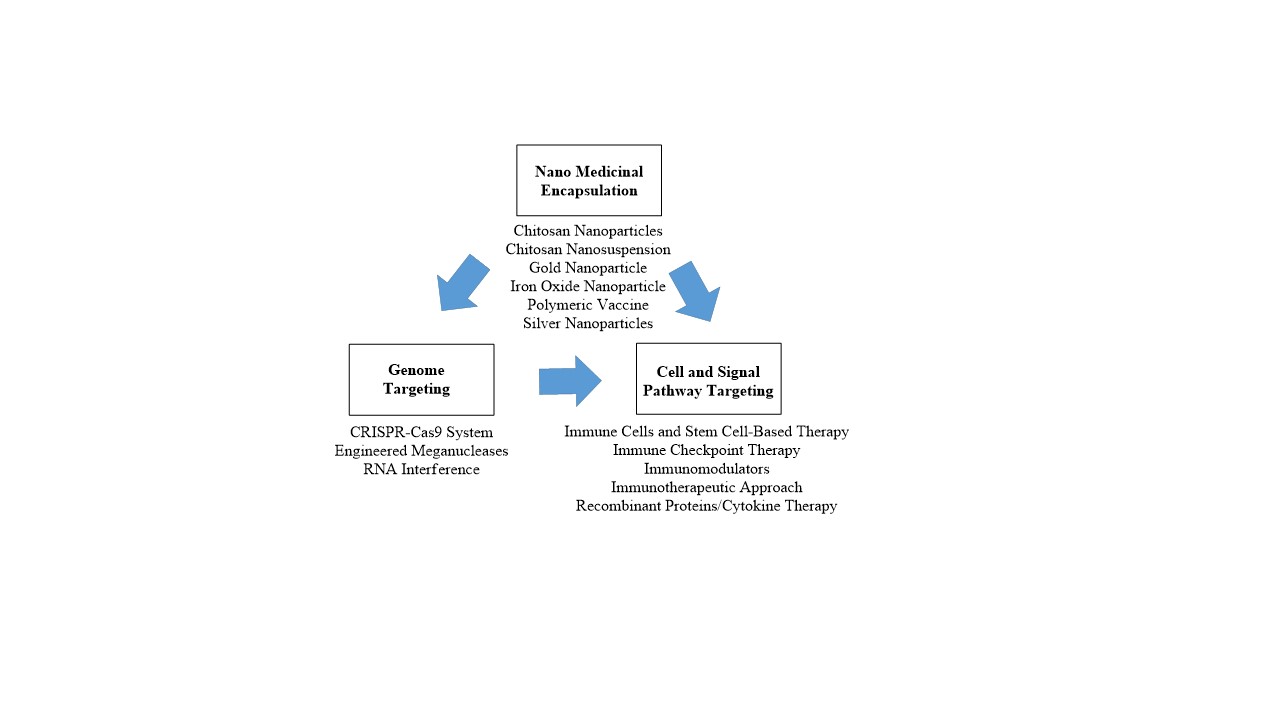
The treatment of parasitic diseases is multifaceted. The control methods require a complex interplay involving experts in public health, government policies, education, and medical sciences. Several strategies used in the treatment of parasitic diseases are considered and they are based on the availability, effectiveness, affordability, and acceptability of the used drug. Other measures include effective elimination of vector, and animal reservoirs. Interestingly, new strategies and approaches for the treatment of parasitic diseases involve nanomedical encapsulation of drugs and active compounds. Furthermore, genome, cells, and signal pathways targeting have been used for preventing and treating parasitic diseases. These approaches are used for diagnosis, and treatments of disease and to gain increased understanding of underlying disease mechanisms. Phytocompounds such as flavonoids and others are used in nanotherapeutics for treating parasitic diseases as they prevent oxidation of a liable substrate in a system, among other beneficial properties. Therefore, the present review highlights the use of several phytocompounds in nanotherapeutics to treat diseases caused by parasites.
References
Abulaihaiti, M., Wu, X-W., Qiao, L., Lv, H-L., Zhang, H-W., Aduwayi, N., et al. (2015). Efficacy of albendazole-chitosan microsphere-based treatment for alveolar echinococcosis in mice. PLoS neglected tropical diseases. 9(9): e0003950.
Adekiya, T. A., Kondiah, P., Choonara, Y. E., Kumar, P., and Pillay, V. (2020). A Review of Nanotechnology for Targeted Anti-schistosomal Therapy. Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology. 8: 32.
Ahmed, S., Ahmad, M., Swami, B.L., and Ikram, S. (2016). A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: A green expertise. J Adv. Res. 7(1): 17–28.
Ahmed, S.A., El-Mahallawy, H.S. and Karanis, P. (2019). Inhibitory activity of chitosan nanoparticles against Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts. Parasitology Research. 118(7): 2053-2063.
Allahverdiyev, A.M., Abamor, E.S., Bagirova, M., Ustundag, C.B., Kaya, C., Kaya, F., et al. (2011). Antileishmanial effect of silver nanoparticles and their enhanced antiparasitic activity under ultraviolet light. International journal of Nanomedicine. 6: 2705.
Baranwal, A., Srivastava, A., Kumar, P., Bajpai, V.K., Maurya, P.K., Chandra, P. (2018). Prospects of nanostructure materials and their composites as antimicrobial agents. Front Microbiol. 9: 422.
Bavand, Z., Gholami, S., Honary, S., Rahimi, E.B., Torabi, N., Barabadi, H. (2014). In vitro evaluation of the effect of gold nanoparticles on Giardia lamblia cyst. 16(10): 79.
Bharali, D.J., Mousa, S.A. (2010). Emerging nanomedicines for early cancer detection and improved treatment: current perspective and future promise. Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 128: 324e335.
Boomi, P., Ganesan, R., Prabu Poorani, G., Jegatheeswaran, S., Balakumar, C., Gurumallesh Prabu, H., Anand, K., Marimuthu Prabhu, N., Jeyakanthan, J., and Saravanan, M. (2020). Phyto-Engineered Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs) with Potential Antibacterial, Antioxidant, and Wound Healing Activities Under in vitro and in vivo Conditions. Int J Nanomedicine. 15: 7553–7568.
Boomi, P., Prabu, H. (2013). Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial analysis of polyaniline/Au-apdnanocomposite. Colloids surf a physicochem Eng Asp. 429:51-59.
Brodaczewska, K., Wolaniuk, N., Donskow-Lysoniewska, K., Doligalska, M. (2013). Chitosan stimulates lymphocyte proliferation during the muscle phase of Trichinella spiralis infection in mice. Front Immunol Conference Abstract: 15th International Congress of Immunology (ICI).
Cioli, D., Pica-Mattoccia, L., Basso, A., and Guidi, A. (2014). Schistosomiasis control: praziquantel forever? Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 195: 23–29.
da Paixão Siqueira, L., Fontes, D. A. F., Aguilera, C. S. B., Timóteo, T. R. R., Ângelos, M. A., Silva, L. C. P. B. B., et al. (2017). Schistosomiasis: drugs used and treatment strategies. Acta Trop. 176: 179–187.
Destura, R.V., Cena, R.B., Galarion, J.H., et al. (2015). Advancing Cryptosporidium Diagonistics from Bench to Bedside. Curr Trop Med Rep., 2:150-160.
Dolman, M.E., Harmsen, S., Storm, G., Hennink, W.E., Kok, R.J. (2010). Drug targeting to the kidney. Advances in the active targeting of therapeutics to proximal tubular cells. Adv Drug Deliv Rev., 62(14): 1344-57.
Gaafar, M., Mady, R., Diab, R., Shalaby, T.I. (2014). Chitosan and silver nanoparticles: promising anti-toxoplasma agents. Experimental parasitology. 143:30-8.
Geethalakshmi, R. and Sarada, D. (2012). Gold and silver nanoparticles from Trianthema decandra: synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial properties. Int. J Nanomed. 7: 5375–5384.
Gherbawy, Y.A., Shalaby, I.M., El-sadek, M.S.A., Elhariry, H.M., Banaja, A.A. (2013). The anti-fasciolasis properties of silver nanoparticles produced by Trichoderma harzianum and their improvement of the anti-fasciolasis drug triclabendazole. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 14(11):21887-98.
Ghorbal, M., Gorman, M., Macpherson, C. R., Martins, R. M., Scherf, A., and Lopez-Rubio, J. J. (2014). Genome editing in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nature Biotechnology. 32(8):819-821.
Hassan, S.T.S., Berchova, K. and Sudomova, M. (2015). Antimicrobial, antiparasitic and anticancer properties of Hibiscus sabdariffa (L.) and its phytochemicals: in vitro and in vivo studies. 65: 10-14.
Holthof, J.H., Wang, Z., Seely, K.A., Golden, N., Mayeux, P.R. (2012). Resveratol improves renal microcirculation, protects the tubular epithelium, and prolongs survival in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Kidney int 81(4):370-8.
Jameii, F., DalimiAsl, A., Karimi, M., Ghaffarifar, F. (2015). Healing Effect Comparison of Selenium and Silver Nanoparticles on Skin Leishmanial Lesions in Mice. Scientific Journal of Hamadan University of Medical Sciences. 22(3):217-23.
Kareem, Hatam-Nahavandi (2019). Some Application of Nonobiotechenology in Parasitology. Iranian Journal of Public Health. 48(9): 1758-1759.
Karimi, M., Dalimi, A., Jamei, F., Ghaffarifar, F., Dalimi, A. (2015). The Killing effect of Silver Nanoparticles and Direct Electric Current Induction on Leishmania major Promastigotes In Vitro. 18 (3) :87-96.
Khosravi, A., Sharifi, I., Barati, M., Zarean, M., Hakimi-Parizi, M. (2011). Anti-leishmanial effect of nanosilver solutions on Leishmania tropicapromastigotes by in-vitro assay. Zahedan Journal of Research in Medical Sciences. 13(7):8-12.
Leiby, D. A., O'Brien, S. F., Wendel, S., Nguyen, M. L., Delage, G., Devare, S. G., Hardiman, A., Nakhasi, H. L., Sauleda, S., Bloch, E. M., & WPTTID Subgroup on Parasites (2019). International survey on the impact of parasitic infections: frequency of transmission and current mitigation strategies. Vox Sang 114(1): 17 – 27.
Lima, N. M., de Marqui, S. R., Andrade, T., and Silva, D. (2020). Phytochemical, metabolic profiling and antiparasitic potential from Inga semialata leaves (Fabaceae). Natural product research, 1–6.
Mahato, K. et al. (2016). in Techno-Societal 2016. “International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Societal Applications. 421–431.
Mahato, K., Kumar, A., Maurya, P.K., Chandra, P. (2017). Shifting paradigm of cancer diagnoses in clinically relevant samples based on miniaturized electrochemical nanobiosensors and microfluidic devices. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 100: 411e428.
Marc Ouellette (2001). Biochemical and molecular mechanisms of drug resistance in parasites. Tropical Medicine and International Health. 6(11): 874- 882.
Mathers, C.D. (2020). History of global burden of disease assessment at the World Health Organization. Arch Public Health 78: 77.
Maude, R.J., Woodrow, C.J., White, L.J. (2010). ArtemisininAntimalarials: Preserving the “Magic Bullet”. Drug Dev. Res., 71: 12–19.
Mohapatra, S.C., Tiwari, H.K., Singla, M., Rathi, B., Sharma, A., Mahiya, K., et al. (2010). Antimalarial evaluation of copper (II) nanohybrid solids: inhibition of plasmepsin II, a hemoglobin-degrading malarial aspartic protease from Plasmodium falciparum. JBIC Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry. 15(3):373-85.
Mukherjee, S., Mukherjee, N., Gayen, P., Roy, P., and Sinha Babu DS.P. (2016). Metabolic Inhibitors as Antiparasitic Drugs: Pharmacological, Biochemical and Molecular Perspectives. Current Drug Metabolism. 17(10).
Murray, C.J.L. (1996). Global burden of disease and injury series the global burden of disease a comprehensive assessment of mortality and disability from diseases, injuries, and risk factors in 1990 and projected to 2020 edited by Christopher. L. Murray Harvard University Boston, MA, USA.
Nayak, A.P., Tiyaboonchai, W., Patankar, S., Madhusudhan, B., Souto, E.B. (2010). Curcuminoids-loaded lipid nanoparticles: novel approach towards malaria treatment. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces. 81(1):263-73.
Newman, D.J., Cragg, G.M. (2016). Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs from 1981 to 2014. J Nat Prod. 79(3):629-61.
Noh, H.-B., Lee, K.-S., Chandra, P., Won, M.-S., Shim, Y.-B. (2012). Application of a CueCo alloy dendrite on glucose and hydrogen peroxide sensors. Electrochemica Acta 61:36e43.
Norouzi, R. (2017). A review on Most Nanoparticles Applied Against Parasitic Infections. J. Biol. Today's World. 6 (10): 196-203.
Nwaka, S. and Ridley, R. G. (2003). Virtual drug discovery and development for neglected diseases through public private partnerships. Nature Rev. Drug Discov. 2: 919–928.
Parboosing, R., Maguire, G. E., Govender, P., and Kruger, H. G. (2012). Nanotechnology and the treatment of HIV infection. Viruses. 4(4): 488–520.
Piperaki, E.T., Tassios, P.T. (2016). Parasitic infections; their position and impact in the postindustrial world. Clin Microbiol Infect. 22: 469 – 470.
Pisarski, K. (2019). The global burden of disease of zoonotic parasitic diseases: top 5 contenders for priority consideration. Trop Med Infect Dis 4:2-9.
Ponarulselvam, S., Panneerselvam, C., Murugan, K., Aarthi, N., Kalimuthu, K., Thangamani, S. (2012). Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaves of Catharanthus roseus Linn. G. Don and their antiplasmodial activities. Asian Pacific journal of tropical biomedicine. 2(7):574-80.
Rezaei, R., Safaei, M., Mozaffari, H. R., Moradpoor, H., Karami, S., Golshah, A., Salimi, B., and Karami, H. (2019). The Role of Nanomaterials in the Treatment of Diseases and Their Effects on the Immune System. Open access Macedonian journal of medical sciences. 7(11): 1884–1890.
Richardson, L.L., Adler, L.S., Leonard, A.S., Andicoechea, J., Regan, K.H., Anthony, W.E., Manson, J.S. and Irwin, R.E. (2015). Secondary metabolites in floral nectar reduce parasite infections in bumblebees. Proc. R. Soc. B 282: 20142471.
Roscigno, G., Puoti, I., Giordano, I., Donnarumma, E., Russo, V., Affinito, A., Adamo, A., Quintavalle, C., Todaro, M., Vivanco, M. D., and Condorelli, G. (2017). MiR-24 induces chemotherapy resistance and hypoxic advantage in breast cancer. Onco target. 8(12): 19507–19521.
Saad, H., Soliman, M.I., Azzam, A.M., Mostafa, B. (2015). Antiparasitic activity of silver and copper oxide nanoparticles against Entamoeba histolytica and Cryptosporidium parvum cysts. J Egypt Soc Parasitol. 45(3): 593-602.
Said, D.E., Elsamad, L.M., Gohar, Y.M. (2012). Validity of silver, chitosan, and curcumin nanoparticles as antiGiardia agents. Parasitology Research. 111(2):545-554.
Salah-Tazdaït, R., Tazdaït, D., Harrat, Z., Eddaikra, N., Abdi, N., Mameri, N. (2015). Antiparasite Activity of Chitosan. Proceedings of 2015 International Conference on Chemical, Metallurgy and Environmental Engineering, Istanbul, Turkey. 277–280.
Sazgarnia, A., Taheri, A.R., Soudmand, S., Parizi, A.J., Rajabi, O., Darbandi, M.S. (2013). Antiparasitic effects of gold nanoparticles with microwave radiation on promastigotes and amastigotes of Leishmania major. International Journal of Hyperthermia. 29(1):79-86.
Schmidt, T. J., Khalid, S. A., Romanha, A. J., Alves, T. M., Biavatti, M. W., Brun, R., Da Costa, F. B., de Castro, S. L., Ferreira, V. F., de Lacerda, M. V., Lago, J. H., Leon, L. L., Lopes, N. P., das Neves Amorim, R. C., Niehues, M., Ogungbe, I. V., Pohlit, A. M., Scotti, M. T., Setzer, W. N., de N C Soeiro, M., de N.C., Steindel M. and Tempone, A. G. (2012). The potential of secondary metabolites from plants as drugs or leads against protozoan neglected diseases - part I. Current medicinal chemistry, 19(14), 2128–2175.
Sedighi, F., Abbasali, P.R., Maghsood, A., Fallah, M. (2016). Comparison of therapeutic effect of anti-cryptosporidium nano-nitazoxanide (NTZ) with free form of this drug in neonatal rat. Avicenna J Clin Med. 23 (2) :134-140.
Sen, R., Bandyopadhyay, S., Dutta, A., Mandal, G., Ganguly, S., Saha, P., Chatterjee, M. (2007). Artemisinin triggers induction of cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in Leishmania donovani promastigotes. J. Med. Microbiol. 56: 1213-1218.
Shah, M., Fawcett, D., Sharma, S., Tripathy, S. K., and Poinern, G. (2015). Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles via Biological Entities. Materials (Basel, Switzerland), 8(11), 7278–7308.
Singer, M.S., Farkas, T.E., Skorik, C.M. and Mooney, KA. (2012). Tritropic interactions at a community level: effect of host plant species quality on bird predation of caterpillars. Am. Nat. 179: 363-374.
Singh, B. (2020). Molecular Medicines for Parasitic Diseases. Methods in Molecular Medicine. 1-12.
Singh, L., Kruger, H. G., Maguire, G., Govender, T., and Parboosing, R. (2017). The role of nanotechnology in the treatment of viral infections. Therapeutic advances in infectious disease. 4(4): 105–131.
Smith Darr, J., Conn, D.B. (2015). Importation and transmission of parasitic and other infectious diseases associated with international adoptee and refugee immigrating into the United State of America. Biomed Res Int. 763-715.
Soriano, M.L., Rodriguez-Benot, A., Valcarcel, M. (2018). Nanotechnological functions of a new nephrology. Nefrologia 38(4): 368-78.
Swargiary, A., Daimari, A., Daimari, M., Basumatary, N., and Narzary, E. (2016). Phytochemicals, antioxidant, and anthelmintic activity of selected traditional wild edible plants of lower Assam. Indian J Pharmacol. 48(4): 418–423.
Thirumurugan, D., Cholarajan, A., Raja Suresh, S.S. and Vijayakumar, R. (2018). An Introductory Chapter: Secondary Metabolites, Secondary Metabolites - Sources and Applications. DOI: 10.5772/intechopen.79766. Available from: https://www.intechopen.com/books/secondary-metabolites-sources-and-applications/an-introductory-chapter-secondary-metabolites Accessed November, 2021.
Tijjani, H., Egbuna, C. and Luka, C.D. (2018). Biosynthesis of Phytochemicals, In Phytochemistry, Volume 1, Chapter 2, Fundamentals, Modern Techniques, and Applications, Apple Academic Press Inc. Canada. 37-78.
Torgerson, P.R., Devleesschauwer, B., Praet, N., Speybroeck, N., Willingham, A.L., Kasuga, F., et al. (2015). World Health Organization Estimates of the Global and Regional Disease Burden of 11 Foodborne Parasitic Diseases, 2010: A Data Synthesis. PLoS Med 12(12).
Tripathy, S., Das, S., Chakraborty, S.P., Sahu, S.K., Pramanik, P., Roy, S. (2012). Synthesis, characterization of chitosan–tripolyphosphate conjugated chloroquine nanoparticle and its in vivo anti-malarial efficacy against rodent parasite: A dose and duration dependent approach. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 434(1): 292-305.
Van Wyk, B.E., Wink M. (2004). Medicinal Plants of the World: An Illustrated Scientific Guide to Important Medicinal Plant and Their Uses. Timber Press: Portland, OR, USA.
Venier-Julienne, M., Vouldoukis, I., Monjour, L., Benoit, J. (1995). In vitro study of the anti-leishmanial activity of biodegradable nanoparticles. Journal of drug targeting. 3(1):23-9.
Ventola, C. L. (2012). The nanomedicine revolution: part 1: emerging concepts. P&T : a peer-reviewed journal for formulary management. 37(9): 512–525.
Wagner, J. C., Platt, R. J., Goldfless, S. J., Zhang, F., and Niles, J. C. (2014). Efficient CRISPR-Cas9-mediated genome editing in Plasmodium falciparum. Nature methods. 11(9), 915–918.
Watkins, B.M. (2003). Drugs for the control of parasitic diseases: current status and development TRENDS in Parasitology, 19:11: 477 – 478.
Wink, M. (2012). Medicinal Plants: A Source of Anti-parasitic Secondary Metabolites. Molecules. 17(11): 1277-12791.
Xu, Y., Hu, N., Jiang, H.F., Zheng, D.H. (2016). Cercumin carrying nanoparticles prevent ischemia-reperfusion injury in human renal cells. Onchotarget 7(52): 87390-401.
Yu, H., Liu, D., Shu, G., Jin, F., and Du, Y. (2020). Recent advances in nanotherapeutics for the treatment of acute kidney injury. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16(4):432-443.
Yu, M., Liu, J., Ning, X., Zheng, J. (2015). High-contrast noninvasive imaging of kidney kinetics enabled by renal clearable nanofluorophores. Angewchemint Ed Engl. 54(51): 15434-8.
Zahir, A. A., Chauhan, I. S., Bagavan, A., Kamaraj, C., Elango, G., Shankar, J., Arjaria, N., Roopan, S. M., Rahuman, A. A., and Singh, N. (2015). Green Synthesis of Silver and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Using Euphorbia prostrata Extract Shows Shift from Apoptosis to G0/G1 Arrest followed by Necrotic Cell Death in Leishmania donovani. Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 59(8), 4782–4799.
Zapalski, M.K., Hubert, B.L.M. (2011). First fossil record of parasitism in Devonian calcareous sponges (stromatoporoids). Parasitology. 138: 132-138.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Gadau Journal of Pure and Allied Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

