PHARMACOLOGY OF SPONDIAS MOMBIN IN LIVER CANCER TREATMENT AND TOXICITY EVALUATION
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54117/gjpas.v3i1.4Keywords:
Cancer, Liver, Pharmacology, ToxicityAbstract
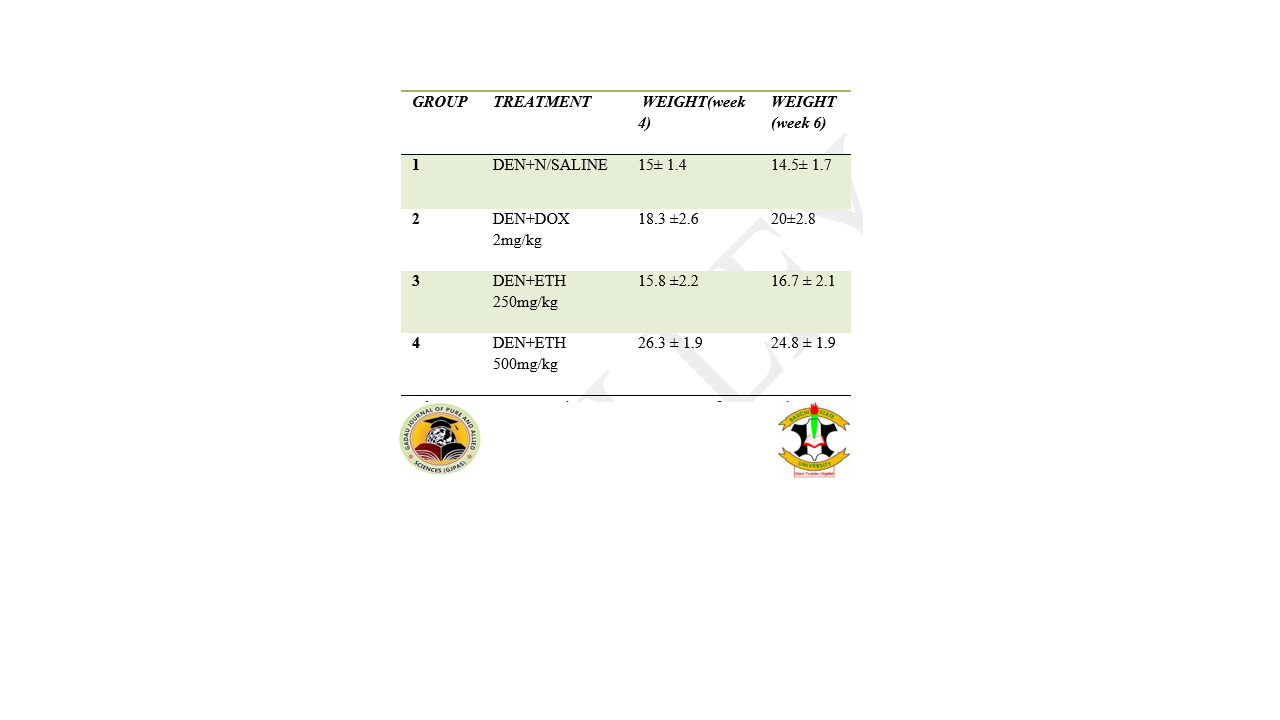
Cancer is among the major causes of death in the world. Spondias mombin is a natural product being accepted as medication for many diseases. This research aimed at evaluating the toxicity potential and pharmacology properties of Spondias mombin leaves in liver cancer treatment. Spondias mombin leaves were shade dried at room temperature and size reduced to powder and extracted using cold maceration. Phytochemical screening of the plant extract was conducted. Six weeks of healthy mice; weighing 22-25g were used. For acute toxicity studies, ten mice were grouped into a normal control group and another group received 2000mg/kg of the extract. The animals were observed closely for 14 days. Twenty-four mice were divided into 4 groups. One group served as control and received only saline at 10mls/kg and the other groups received one percent diethylnitrosamine (DEN) given via peritoneal injection to the mice weekly at a dose of 35mg/kg for six weeks. The remaining three groups received 250 mg/kg, 500 mg, and doxorubicin 2 mg/kg after four weeks of induction. The treatment commenced with the extract while still giving the DEN for cancer induction. The phytochemical analysis shows the presence of alkaloids, cardiac glycosides, saponins, tannins, phenolic compounds, steroids, flavonoids, and terpenoids, and the absence of carbohydrates anthraquinones. Animals exposed to the extract and observed for 14 days exhibited no obvious sign of toxicity with zero mortality during the period of observation. There is a slight weight change among the control group between 20.8±3.56 to 25.63 2.60.The creatinine, CL, and HCO3 of the control significantly (P˂0.005) differed from the study groups. There was a slight increase in weight after the first dose, though a steady decrease was noticed following the second, third, and fourth doses of DEN in the mice. ALT and AST were higher in the extract-treated groups compared to both Dox-treated and saline-treated groups. The extract was shown to have no obvious physical sign of toxicity and it doesn’t cause mortality in all the tested animals. Ethanol extract of the plant reversed the loss in weight, deterioration in liver enzymes, and protein production to an extent similar to that of standard anti-cancer agents.
References
Abo K.A., Ogunleye V.O., Ashidi J.S. (1999). Antimicrobial potential of Spondiasmombin, Croton zambesicus and Zygotritoniacrocea. Phytother Research. (6):494-7.
Alexandru, B., Iasmina, M., Dorina, C., Florin, H., Cristina, A.D. and Octavian M.C. (2021). Experimental Models of Hepatocellular Carcinoma—A Preclinical Perspective. Cancers (Basel). 13(15): 3651.
Ali, M., Wani, S.U.D., Salahuddin, M., S N M, K M, Dey, T., Zargar, M.I., Singh, J. (2023). Recent advance of herbal medicines in cancer- a molecular approach. Heliyon. 2023 Feb 14;9(2):e13684.
Al-Khayri J.M., Sahana G.R., Nagella P., Joseph B.V., Alessa F.M., Al-Mssallem M.Q. (2022). Flavonoids as Potential Anti-Inflammatory Molecules: A Review. Molecules. 27(9):2901.
Anwanwan D., Singh S.K., Singh S., Saikam V., Singh R. Challenges in liver cancer and possible treatment approaches. BiochimBiophysActa Rev Cancer. 1873(1):188314.
Arboatti, A.S., Lambertucci, F., Sedlmeier, M.G., Pisani, G., Monti, J., Álvarez, M.L., Francés, D., Ronco, M.T., Carnovale, C.E. (2018). Diethylnitrosamine Increases Proliferation in Early Stages of Hepatic Carcinogenesis in Insulin-Treated Type 1 Diabetic Mice. Biomedical Research Int. 9472939.
Ashwin, A., Veena, G., and Kia, S. (2006). Epidemiology of Primary and Secondary Liver Cancers. Semin Intervent Radiology. 23(1): 47–63.
Brown, Z.J., Heinrich, B. and Greten, T. F. (2018). Mouse models of hepatocellular carcinoma: an overview and highlights for immunotherapy research. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 15, 536–554.
Chang M.H. (2011). Hepatitis B virus and cancer prevention. Recent Results Cancer Research. 188:75-84.
Cullen, K., Jones, M., Pockett, R.D., Burton, A., Cross, T.J.S., Rowe, I.A., Paley, L., Tataru, D., Alexander, G., Marshall, A., Fitzsimmons, D. (2023). Cost of hepatocellular carcinoma to the National Health Service in England: a registry-based analysis. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 10(1) e000998
Divekar P.A., Narayana S., Divekar B.A., Kumar R., Gadratagi B.G., Ray A., Singh A.K., Rani V., Singh V., Singh A.K., Kumar A., Singh R.P., Meena R.S., Behera T.K. (2022). Plant Secondary Metabolites as Defense Tools against Herbivores for Sustainable Crop Protection. Internal Journal Molecular Science. 23(5):2690.
Duspara K., Bojanic K., Pejic J.I., Kuna L., Kolaric T.O., Nincevic V., Smolic R., Vcev A., Glasnovic M., Curcic I.B., Smolic M. (2021). Targeting the Wnt Signaling Pathway in Liver Fibrosis for Drug Options: An Update. Journal of ClinicalTranslHepatology. 9(6):960-971.
El-Zayat, S.R., Sibaii, H. and El-Shamy, K.A. (2019). Physiological process of fat loss. Bull Natl Res Cent 43, 208 (2019).
Farmer, D.G., Rosove, M.H., Shaked, A., Busuttil, R.W. (1994). Current treatment modalities for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 219(3):236-47.
Fuchs T.C., Hewitt P. (2011). Biomarkers for drug-induced renal damage and nephrotoxicity-an overview for applied toxicology. AAPS J. 2011 Dec;13(4):615-31.
Gowda S., Desai P.B., Kulkarni S.S., Hull V.V., Math A.A., Vernekar S.N. (2010). Markers of renal function tests. N Am J Med Sci. 2010 Apr;2(4):170-3.
Hällfin J.& Laurell C.B. (1972). Plasma Protein Pattern in Cirrhosis of the Liver, Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation, 29:sup124, 97-103
Harriet R., Melina A., Jacques F., Olufunmilayo L., Citadel J.C., Jérôme V., Mathieu L., Katherine A.M., Isabelle S. (2022). Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to 2040. Journal of Hepatology vol. 77 j 1598–1606
José M. P., Miren G., Antonio S., María I.L., Raúl J.A. (2022). Recreational Drugs and the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 14(21):5395
Ju D.Y., Pierre H., Gregory J.G., Amina A., Amelie P., Lewis R.R. (2019). A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 16(10):589-604.
Kaplan, D.E., Chapko, M.K., Mehta, R., Dai, F., Skanderson, M., Aytaman, A., Baytarian, M., D'Addeo, K., Fox R., Hunt, K., Pocha C., Valderrama A., Taddei T.H. (2018). VOCAL Study Group. Healthcare Costs Related to Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Among Veterans With Cirrhosis in the United States. Clinical Gastroenterol Hepatol. 16(1):106-114.e5.
Keisuke H., Izumi Y., Yuichi H., Sohji N. (2022). Iron and liver cancer: an inseparable connection. The FEBS Journal Volume289, Issue24 Pages 7810-7829
Liu, C.Y., Chen, K.F., Chen, P.J. (2015). Treatment of Liver Cancer. Cold Spring HarbPerspect Med. 5(9):a021535.
Llovet, J.M., Kelley, R.K., Villanueva, A. (2021). Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. vol 7, 6.
Marrelli M., Conforti F., Araniti F., Statti G.A. (2016). Effects of Saponins on Lipid Metabolism: A Review of Potential Health Benefits in the Treatment of Obesity. Molecules. 21(10):1404.
Maud L., Mark R.T. (2017). Battlefield against hepatitis B infection and HCC in African Journal Hepatoly 66(3):645-654.
Momin B., Millman A.J., Nielsen D.B., Revels M., Steele C.B. (2018). Promising practices for the prevention of liver cancer: a review of the literature and cancer plan activities in the National Comprehensive Cancer Control Program. Cancer Causes Control. (12):1265-1275.
Njoku P.C. and AkumefulaM.I. (2007). Phytochemical and Nutrient Evaluation of SpondiasMombin Leaves. Pakistan Journal of Nutrition, 6: 613-615.
NwaogwugwuJ., Friday U., Okereke S., Egege A., Atasi O. (2018). Toxicological Evaluation of aqueous leaf extract of Spondiasmombin using albino rat. Journal of Medicinal Herbs and Ethnomedicine 2018, 4: 23-30
Ogunro O.B., Oyeyinka B.O., Gyebi G.A., Batiha G.E. (2023). Nutritional benefits, ethnomedicinal uses, phytochemistry, pharmacological properties and toxicity of Spondiasmombin Linn: a comprehensive review. Journal Pharm Pharmacology 75(2):162-226.
Okeke, E., Davwar, P. M., Roberts, L., Sartorius, K., Spearman, W., Malu, A., and Duguru, M. (2020). Epidemiology of Liver Cancer in Africa: Current and Future Trends. Seminars in Liver Disease, 40(2), 111–123.
Olalekan B. O., Barnabas O. O., Gideon A.G., Gaber E.B. (2023). Nutritional benefits, ethnomedicinal uses, phytochemistry, pharmacological properties and toxicity of Spondiasmombin Linn: a comprehensive review, Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, Volume 75, Issue 2, Pages 162–226
Olukemi A., Omotola K.B.(2014). Efficacy of fresh leaf extracts of Spondiasmombin against some clinical bacterial isolates from typhoid patients, Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Disease,Volume 4, Issue 6,2014,Pages 442-446,
Osuntokun O.T. (2019) Exploring the Medicinal Efficacy, Properties and Therapeutic uses of Spondiasmombin (Linn) International Journal of Applied Research Medicinal Plants 2: 115.
Pranshant, T., (2011). Phytochemical screening and Extraction: A Review. Internationale Pharmaceutical Sciencia 1.1 (2011): 98- 106
Prashant T., Bimlesh K., Mandeep K., Gurpreet K., Harleen K. (2011). Phytochemical screening and Extraction: A Review. InternationalepharmaceuticascienciaVol. 1 Issue 1
Qianru L., Maomao C., Lin L., Fan Y., He Li., Xinxin Y., Siyi He., Shaoli Z., Yi T., Changfa X. and Wanqing C. (2022). Burden of liver cancer: From epidemiology to prevention. Chin J Cancer Research. 34(6): 554–566.
Rogos R. (1978). UntersuchungenzumVerhalten von Albumin beiakuten und chronischenLeberschäden I. Das Verhalten von Albumin während der EntwicklungzurThioazetamidzirrhose der Ratte [The behavior of albumin in acute and chronic liver diseases. I. The behavior of albumin during the development of rat thioacetamide cirrhosis]. Z Gesamte Inn Med. 1978 Jun 15;33(12):388-94.
Salgia R., Mendiratta V. (2021). The Multidisciplinary Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clinical Liver Disease (Hoboken). 17(6):405-408.
Sameh S., Al-Sayed E., Labib R.M., Singab A.N. (2018). Genus Spondias: A Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018:5382904.
Singh A.K., Singh S.V., Kumar R., Kumar S., Senapati S., Pandey A.K. (2023). Current therapeutic modalities and chemopreventive role of natural products in liver cancer: Progress and promise. World JournalHerpetology. 15(1):1-18.
Tavakoli J., Miar S., Majid Zadehzare M., Akbari H. (2012). Evaluation of effectiveness of herbal medication in cancer care: a review study. Iran Journal Cancer Prev. 5(3):144-56. PMID: 25628834
Tufoni M., Zaccherini G., Caraceni P., Bernardi M. (2020). Albumin: Indications in chronic liver disease. United European Gastroenterol Journal. 8(5):528-535.
Uchendu C.N., Isek T. (2008). Antifertility activity of aqueous ethanolic leaf extract of Spondiasmombin (Anacardiaceae) in rats. African Health Science. 8(3):163-7.
Vierboom Y.C., Preston S.H., Stokes A. (2018). Patterns of weight change associated with disease diagnosis in a national sample. PLoS One. 2018 Nov 26;13(11):e0207795. improve food security. In Reference Module in Food Science, pp 1–9.
Solomon, A. (2010). Estimating Welfare Effect of Modern Agricultural Technologies: A Micro-Perspective from Tanzania and Ethiopia. International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT), Nairobi, Kenya.
Solomon, A., Bekele, S., Franklin, S. and Mekbib, G. H. (2011). Agricultural technology adoption, seed access constraints and commercialization in Ethiopia. Journal of Development and Agricultural Economics., 3(9):436–447.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Gadau Journal of Pure and Allied Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

