Flavonoid-rich extract of unripe Terminalia catappa Modulates Redox Status and Aging in Lead-Induced Neuro-genotoxic Drosophila
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54117/gjpas.v3i2.160Keywords:
Drosophila melanogaster, Environmental Toxicant, Lead, Longevity, Neurotoxicity, Terminalia catappaAbstract
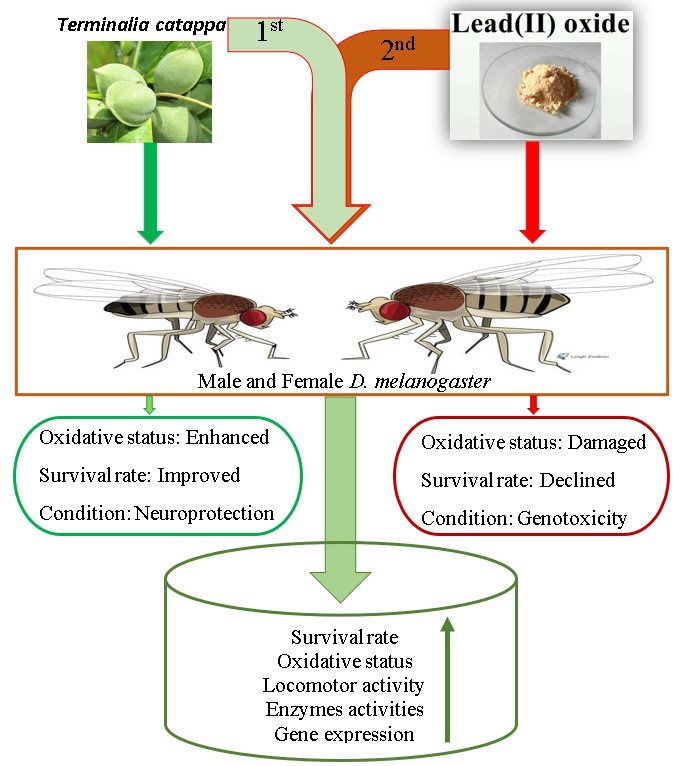
Terminalia catappa (Indian almond) fruit is an oval fruit in shape, growing on a large tree found mostly in the tropical region. The tree has wide health applications and benefits various African and Asian communities. However, there is little documented evidence of its effects on neuroprotection and longevity. This study explored the neuroprotective potential of the flavonoid content from the unripe fruit part of the plant against lead-induced neurogenotoxicity in a fly model (Drosophila melanogaster). Two to three days old male and female flies were harvested and used for the experiment. Negative geotaxis and flies’ pupation assays were employed for the assessment of the flies' behavior. Phase II antioxidant enzymes’ activities and their expression levels were evaluated to ascertain the redox status of the flies before and after the toxicants exposure. Following the effective dose determination assay, 3.0 and 5.0 mg/g diets were found to be highly effective, meanwhile a concentration of 0.1 µg/g diet of lead (Pb) successfully induced neuro and genotoxicity. There was a remarkable improvement in the emergence of new and the locomotor function of the matured flies fed with the extract before their exposure to the toxic environment compared to the control group. Significant increase in the activity of Catalase, Superoxide dismutase (SOD), and Glutathione-s-transferase (GST) with concurrent reduction of AChE activity in the extract pre-fed flies. A similar effect was also recorded in the mRNA expression level of the corresponding genes when evaluated using a polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). The collective findings of the present study revealed the potential neuro and gene protection effect of the studied extract through antioxidant and antiaging enzyme activities against Lead-induced toxicity in D. melanogaster. Showcasing the potential of the fruit as a source of nutraceuticals that could improve the wellness and quality of human lives when further studied.
References
Abd Karim, N. A., Adam, A. H. B., Jaafaru, M. S., Rukayadi, Y., & Abdull Razis, A. F. (2023). Apoptotic potential of glucomoringin isothiocyanate (GMG-ITC) isolated from Moringa oleifera Lam seeds on human prostate cancer cells (PC-3). Molecules, 28(7), 3214.
Abdulwanis Mohamed, Z., Mohamed Eliaser, E., Jaafaru, M. S., Nordin, N., Ioannides, C., & Abdull Razis, A. F. (2020). Neuroprotective Effects of 7-Geranyloxycinnamic Acid from Melicope lunu ankenda Leaves. Molecules, 25(16), 3724.
Abolaji, A. O., Fasae, K. D., Iwezor, C. E., Aschner, M., & Farombi, E. O. (2020). Curcumin attenuates copper-induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. Toxicology Reports, 7, 261-268.
Anand, A., Divya, N., & Kotti, P. (2015). An updated review of Terminalia catappa. Pharmacognosy reviews, 9(18), 93.
Duan, H., Yu, L., Tian, F., Zhai, Q., Fan, L., & Chen, W. (2020). Gut microbiota: A target for heavy metal toxicity and a probiotic protective strategy. Science of the Total Environment, 742, 140429.
Dwivedi, S., Kushalan, S., Paithankar, J. G., D’Souza, L. C., Hegde, S., & Sharma, A. (2022). Environmental toxicants, oxidative stress and health adversities: interventions of phytochemicals. Journal of pharmacy and pharmacology, 74(4), 516-536.
Fasae, K. D., & Abolaji, A. O. (2022). Interactions and toxicity of non-essential heavy metals (Cd, Pb and Hg): lessons from Drosophila melanogaster. Current opinion in insect science, 51, 100900.
Fathima, S. A., Maurya, R., & Naqvi, S. (2023). Oxidative Stress and Metals in Alzheimer’s Disease. In Natural Product-based Synthetic Drug Molecules in Alzheimer's Disease: Therapeutic & Theranostic Agents (pp. 17-41). Springer.
Feng, X., Chen, A., Zhang, Y., Wang, J., Shao, L., & Wei, L. (2015). Central nervous system toxicity of metallic nanoparticles. International journal of nanomedicine, 4321-4340.
Hu, P., Li, K., Peng, X.-X., Kan, Y., Yao, T.-J., Wang, Z.-Y., Li, Z., Liu, H.-Y., & Cai, D. (2023). Curcumin derived from medicinal homologous foods: its main signals in immunoregulation of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. Frontiers in Immunology, 14, 1233652.
Ijomone, O. M., Ifenatuoha, C. W., Aluko, O. M., Ijomone, O. K., & Aschner, M. (2020). The aging brain: Impact of heavy metal neurotoxicity. Critical reviews in toxicology, 50(9), 801-814.
Iorjiim, W. M., Omale, S., Bagu, G. D., Gyang, S. S., & Alemika, E. T. (2020). Moringa oleifera leaf extract extends lifespan and ameliorate HAART drug-induced locomotor, reproductive, and antioxidant deficits in Drosophila melanogaster. drugs 15. drugs, 15(16), 17.
Jaafaru, M. S. (2024). Flavonoids-rich extract of Aframomum melegueta (black pepper) improves antioxidant status and modulates aging process in lead-induced neurotoxic Drosophila melanogaster. EURASIAN JOURNAL OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING, 10(2), 34-45.
Jaafaru, M. S., Abd Karim, N. A., Enas, M. E., Rollin, P., Mazzon, E., & Abdull Razis, A. F. (2018). Protective effect of glucosinolates hydrolytic products in neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs). Nutrients, 10(5), 580.
Jaafaru, M. S., Mohammed, Z. K., & Auta, R. (2024). THE PHENOLIC-RICH FRACTION OF TERMINALIA CATAPPA MODULATED ANTIOXIDANT INDICATORS AND ENHANCED DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER'S LIFESPAN. Science World Journal, 19(3), 617-624.
Jasim, S. A., Altalbawy, F. M. A., Abohassan, M., Oghenemaro, E. F., Bishoyi, A. K., Singh, R. P., Kaur, P., Sivaprasad, G. V., Mohammed, J. S., & Hulail, H. M. (2024). Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) Roles in Inflammation-mediated Diseases; Current Knowledge. Cell Biochem Biophys. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-024-01587-0
Jomova, K., Makova, M., Alomar, S. Y., Alwasel, S. H., Nepovimova, E., Kuca, K., Rhodes, C. J., & Valko, M. (2022). Essential metals in health and disease. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 367, 110173.
Lundblad, R. L., & Price, N. C. (2004). Protein concentration determination. Bioprocess International, 2(1), 38-46.
Mishra, S., Bharagava, R. N., More, N., Yadav, A., Zainith, S., Mani, S., & Chowdhary, P. (2019). Heavy metal contamination: an alarming threat to environment and human health. Environmental biotechnology: For sustainable future, 103-125.
Mitra, S., Chakraborty, A. J., Tareq, A. M., Emran, T. B., Nainu, F., Khusro, A., Idris, A. M., Khandaker, M. U., Osman, H., & Alhumaydhi, F. A. (2022). Impact of heavy metals on the environment and human health: Novel therapeutic insights to counter the toxicity. Journal of King Saud University-Science, 34(3), 101865.
Mohammed, J. S., & Yusuf, J. H. (2023). Proanthocyanidins-Rich Fraction of Tamarindus Indica Maintained Redox Status of Environmental Toxicant-Induced Genotoxicity in Drosophila Melanogaster. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science.
Mohr, S. E. (2018). First in fly: Drosophila research and biological discovery. Harvard University Press.
Moraes, K. C., & Montagne, J. (2021). Drosophila melanogaster: A powerful tiny animal model for the study of metabolic hepatic diseases. Frontiers in Physiology, 12, 728407.
Oyeniran, O. H., Ademiluyi, A. O., & Oboh, G. (2021). Comparative study of the phenolic profile, antioxidant properties, and inhibitory effects of Moringa (Moringa oleifera Lam.) and Almond (Terminalia catappa Linn.) leaves on acetylcholinesterase and monoamine oxidase activities in the head region of Fruitfly (Drosophila melanogaster Meigen) in vitro. Journal of food biochemistry, 45(3), e13401.
Prasad, D. K., Shukla, R., & Ahammad, S. Z. (2024). Pharmaceuticals and personal care products and heavy metals in the Ganga River, India: Distribution, ecological and human health risk assessment. Environ Res, 263(Pt 1), 119993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2024.119993
Rahman, M. M., Rahaman, M. S., Islam, M. R., Rahman, F., Mithi, F. M., Alqahtani, T., Almikhlafi, M. A., Alghamdi, S. Q., Alruwaili, A. S., & Hossain, M. S. (2021). Role of phenolic compounds in human disease: current knowledge and future prospects. Molecules, 27(1), 233.
Rudzińska, M., Parodi, A., Balakireva, A. V., Chepikova, O. E., Venanzi, F. M., & Zamyatnin Jr, A. A. (2020). Cellular aging characteristics and their association with age-related disorders. Antioxidants, 9(2), 94.
Sarkar, C., Quispe, C., Jamaddar, S., Hossain, R., Ray, P., Mondal, M., Mohamed, Z. A., Jaafaru, M. S., Salehi, B., & Islam, M. T. (2020). Therapeutic promises of ginkgolide A: A literature-based review. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 132, 110908.
Shilpa, O., Anupama, K. P., Antony, A., & Gurushankara, H. P. (2021). Lead (Pb) induced oxidative stress as a mechanism to cause neurotoxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. Toxicology, 462, 152959.
Valenti, M. T., Bertoldo, F., Dalle Carbonare, L., Azzarello, G., Zenari, S., Zanatta, M., Balducci, E., Vinante, O., & Cascio, V. L. (2006). The effect of bisphosphonates on gene expression: GAPDH as a housekeeping or a new target gene? BMC cancer, 6, 1-7.
Vellingiri, B., Suriyanarayanan, A., Selvaraj, P., Abraham, K. S., Pasha, M. Y., Winster, H., Gopalakrishnan, A. V., Singaravelu, G., Reddy, J. K., & Ayyadurai, N. (2022). Role of heavy metals (copper (Cu), arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), iron (Fe) and lithium (Li)) induced neurotoxicity. Chemosphere, 301, 134625.
Yu, G., Wu, L., Su, Q., Ji, X., Zhou, J., Wu, S., Tang, Y., & Li, H. (2024). Neurotoxic effects of heavy metal pollutants in the environment: Focusing on epigenetic mechanisms. Environ Pollut, 345, 123563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2024.123563.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Gadau Journal of Pure and Allied Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

