Alpha lipoic acid improved blood glucose level and lipid profile in type-2 diabetic Wistar rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54117/gjpas.v2i2.107Keywords:
Alpha lipoic acid, blood glucose level, lipid profile, type-2 diabetes, hyperglycemiaAbstract
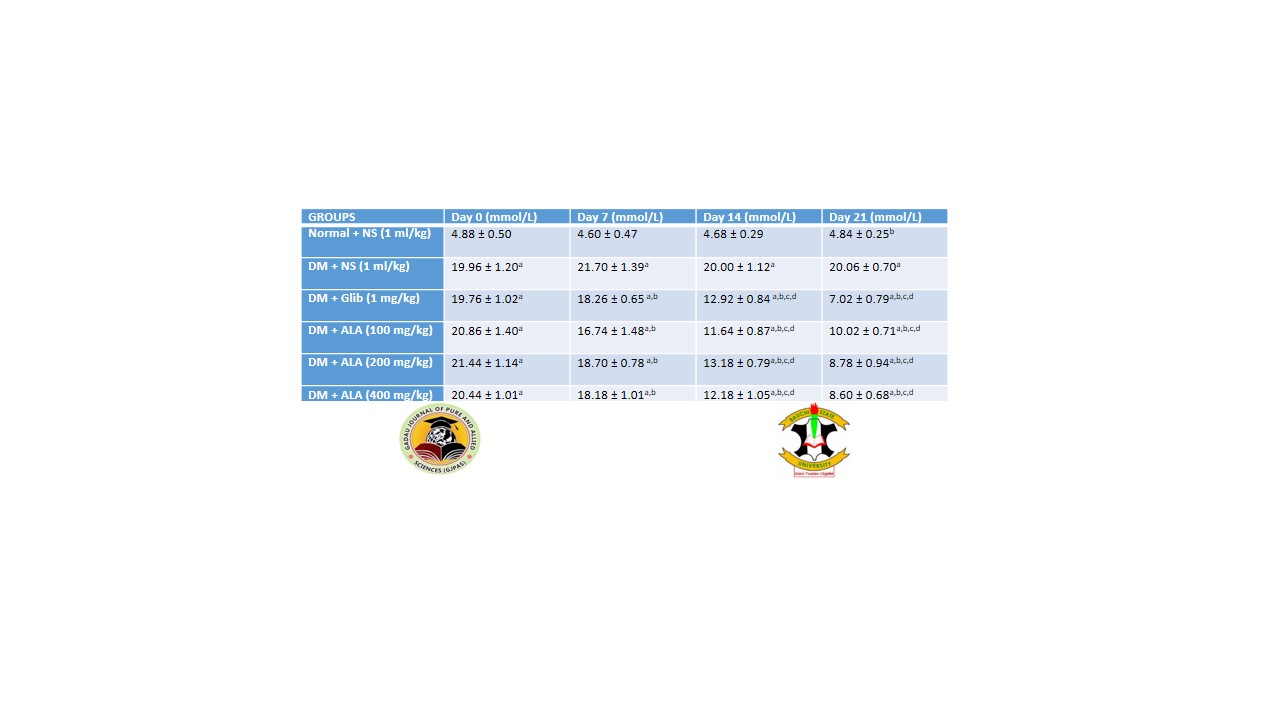
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most common metabolic disorders that is associated with many complications such as dyslipidemia and cardiovascular disease. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of alpha lipoic acid (ALA) on blood glucose levels and lipid profile in type-2 diabetic male Wistar rats. Thirty (30) Wistar rats weighing between 200 – 250 grams were distributed into six groups of five each (n=5). Diabetes was induced using a high-fat diet for eight weeks with a single low dose of streptozotocin (40 mg/kg) intraperitoneally at the end of the sixth week. Group I served as normoglycemic control and received 1 ml/kg normal saline; groups II, III, IV, V, and VI were diabetic and received 1 ml/kg normal saline; glibenclamide 1 mg/kg; ALA 100 mg/kg, ALA 200 mg/kg and ALA 400 mg/kg; respectively. All administrations were done orally for a duration of 21 days. Blood glucose level was determined using the glucose oxidase method. Serum was collected for lipid profile determination. The results obtained from this study showed that ALA across all doses (100 mg/kg, 200 mg/kg, and 400 mg/kg) decreased significantly (p < 0.05) the fasting blood glucose level (10.02 ± 0.71 mmol/L, 8.78 ± 0.94 mmol/L and 8.6 ± 0.68 mmol/L, respectively) when compared to the diabetic control group (20.06 ± 0.70 mmol/L). Lipid profiles were improved with HDL- and LDL- cholesterols increasing and decreasing significantly (42.60 ± 1.66 mg/dL and 1.12 ± 3.68 mg/dL) in the 400 mg/kg ALA group compared to the diabetic untreated group (37.00 ± 2.55 mg/dL and 26.31 ± 2.95 mg/dL, respectively). Therefore, the study demonstrated that ALA has both antihyperglycemic and antilipidemic in type-2 diabetic Wistar rats.
References
Amom, Z., Zakaria, Z., Mohamed, J., Azlan, A., Bahari, H., Baharuldin, M. T. H., Moklas, M. A., Osman, K., Asmawi, Z., and Hassan, M. K. N. (2008). owering Effect of Antioxidant Al p ha -L i p oic Acid in Ex p erimental Atherosclerosis. Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition, 43(September), 88–94.
Ansar, H., Mazloom, Z., Kazemi, F., and Hejazi, N. (2011). Effect of alpha-lipoic acid on blood glucose, insulin resistance, and glutathione peroxidase of type 2 diabetic patients. 98(711), 584–588.
Ariyanti, R. (2019). Dyslipidemia Associated with Hypertension Increases the Risks for Coronary Heart Disease : A Case-Control Study in Harapan Kita Hospital , National Cardiovascular Center , Jakarta. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2517013
Bamidele, O., Ayebatonyo, M., and Davies, C. (2022). Obesity and Dyslipidemia as Risk Factors of Vascular Cognitive Impairment in Adult Hypertensive Nigerian. 34(23), 334–342. https://doi.org/10.9734/JAMMR/2022/v34i234869
Beach, E. F., and Turner, J. J. (1958). An enzymatic method for glucose determination in body fluids. Clinical Chemistry, 4(6), 462–475.
Castillo-Núñez, Y., Morales-Villegas, E., and Aguilar-Salinas, C. A. (2022). Triglyceride-Rich Lipoproteins: Their Role in Atherosclerosis. Revista de Investigacion Clinica; Organo Del Hospital de Enfermedades de La Nutricion, 74(2), 061–070. https://doi.org/10.24875/RIC.21000416
Cremer, D. R., Rabeler, R., Roberts, A., and Lynch, B. (2006). Long-term safety of -lipoic acid ( ALA ) consumption : A 2-year study. 46, 193–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2006.06.003
De MagalhÃes, D. A., Kume, W. T., Correia, F. S., Queiroz, T. S., Allebrandt Neto, E. W., Dos Santos, M. P., Kawashita, N. H., and De França, S. A. (2019). High-fat diet and streptozotocin in the induction of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A new proposal. Anais Da Academia Brasileira de Ciencias, 91(1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765201920180314
Dilworth, L., Facey, A., and Omoruyi, F. (2021). Diabetes mellitus and its metabolic complications: The role of adipose tissues. In International Journal of Molecular Sciences (Vol. 22, Issue 14). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147644
Duch, D. E. (1999). Resin transfer molded high temperature composites. International SAMPE Symposium and Exhibition (Proceedings), 44(10), 1149–1160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2009.07.026.Alpha-lipoic
Elbadawy, A. M., Elmoniem, R. O. A., and Elsayed, A. M. (2021). Alpha lipoic acid and diabetes mellitus : potential effects on peripheral neuropathy and different metabolic parameters. Alexandria Journal of Medicine, 57(1), 113–120. https://doi.org/10.1080/20905068.2021.1907961
Friedewald, W. T., Levy, R. I., and Fredrickson, D. S. (1972). Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clinical Chemistry, 18(6), 499–502.
Galicia-Garcia, U., Benito-Vicente, A., Jebari, S., Larrea-Sebal, A., Siddiqi, H., Uribe, K. B., Ostolaza, H., and Martín, C. (2020). Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus. In International Journal of Molecular Sciences (Vol. 21, Issue 17, pp. 1–34). MDPI AG. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176275
Garkuwa, U. A., Alhassan, A., Tanko, Y., Ibrahim, B., Yakubu, A. B., and Garkuwa, A. H. (2021). Curcumin Improves Serum Electrolytes and Lipid Profiles of Diabetic Wistar Rats. Dutse Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences (DUJOPAS), 7(1), 242–249.
Giri, B., Dey, S., Das, T., Sarkar, M., Banerjee, J., and Dash, S. K. (2018). Chronic hyperglycemia mediated physiological alteration and metabolic distortion leads to organ dysfunction, infection, cancer progression and other pathophysiological consequences: An update on glucose toxicity. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy, 107, 306–328. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.157
Kang, M. J., Lee, E. K., and Lee, S. S. (2004). Effects of two P/S ratios with same peroxidizability index value and antioxidants supplementation on serum lipid concentration and hepatic enzyme activities of rats. Clinica Chimica Acta; International Journal of Clinical Chemistry, 350(1–2), 79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cccn.2004.07.005
Lamarche, B., Moorjani, S., Lupien, P. J., Cantin, B., Bernard, P. M., Dagenais, G. R., and Després, J. P. (1996). Apolipoprotein A-I and B levels and the risk of ischemic heart disease during a five-year follow-up of men in the Québec cardiovascular study. Circulation, 94(3), 273–278. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.94.3.273
Mendoza-núñez, V. M., García-martínez, B. I., Rosado-pérez, J., Santiago-osorio, E., and Pedraza-chaverri, J. (2019). The Effect of 600 mg Alpha-lipoic Acid Supplementation on Oxidative Stress , Inflammation , and RAGE in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3276958
Ormazabal, V., Nair, S., Elfeky, O., Aguayo, C., Salomon, C., and Zuñiga, F. A. (2018). Association between insulin resistance and the development of cardiovascular disease. In Cardiovascular Diabetology (Vol. 17, Issue 1, pp. 1–14). BioMed Central. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-018-0762-4
Petersen, M. C., and Shulman, G. I. (2018). Mechanisms of insulin action and insulin resistance. In Physiological Reviews (Vol. 98, Issue 4, pp. 2133–2223). https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00063.2017
Polonsky, K. S. (2012). The Past 200 Years in Diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine, 367(14), 1332–1340. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmra1110560
Russell, W. R., Baka, A., Björck, I., Delzenne, N., Gao, D., Griffiths, H. R., Hadjilucas, E., Juvonen, K., Lahtinen, S., Lansink, M., Loon, L. Van, Mykkänen, H., Östman, E., Riccardi, G., Vinoy, S., and Weickert, M. O. (2016). Impact of Diet Composition on Blood Glucose Regulation. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 56(4), 541–590. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2013.792772
Serhiyenko, V., Serhiyenko, L., Suslik, G., and Serhiyenko, A. (2018). Alpha-lipoic acid : mechanisms of action and beneficial effects in the prevention and treatment of diabetic complications. 7(4), 174–178. https://doi.org/10.15406/mojph.2018.07.00224
Sobczak, A. I. S., Blindauer, C. A., and Stewart, A. J. (2019). Changes in plasma free fatty acids associated with type-2 diabetes. In Nutrients (Vol. 11, Issue 9, pp. 1–42). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092022
Spiller, S., Blüher, M., and Hoffmann, R. (2018). Plasma levels of free fatty acids correlate with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, 20(11), 2661–2669. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.13449
Sun, Y., Dong, Y., Fan, R., Zhai, L., and Bai, Y. (2012). Effect of ( R ) - ␣ -Lipoic Acid Supplementation on Serum Lipids and Antioxidative Ability in Patients with Age-Related Macular Degeneration. 293–297. https://doi.org/10.1159/000338444
Tabrizi, R., Borhani-Haghighi, A., Mirhosseini, N., Lankarani, K. B., Naghibzadeh-Tahami, A., Akbari, M., Heydari, S. T., Sangari, M., Kolahdooz, F., Raygan, F., and Asemi, Z. (2019). The effects of alpha-lipoic acid supplementation on fasting glucose and lipid profiles among patients with stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. In Journal of Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders (Vol. 18, Issue 2, pp. 585–595). Journal of Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-019-00423-0
Tijjani, H., Danyaro, A. M., Olatunde, A., and Kura, A. U. (2022). Antihyperglycemic activity of verbenone and L-arginine in nicotinamide-streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice: in vitro and in vivo studies. Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 11(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43088-022-00271-7
Vallianou, N., Evangelopoulos, A., and Koutalas, P. (2009). Alpha-lipoic acid and diabetic neuropathy. In Review of Diabetic Studies (Vol. 6, Issue 4, pp. 230–236). https://doi.org/10.1900/RDS.2009.6.230
Vergès, B. (2015). Pathophysiology of diabetic dyslipidaemia: where are we? In Diabetologia (Vol. 58, Issue 5, pp. 886–899). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-015-3525-8
Warraich, H. J., and Rana, J. S. (2017). Dyslipidemia in diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease. In Cardiovascular Endocrinology (Vol. 6, Issue 1, pp. 27–32). https://doi.org/10.1097/XCE.0000000000000120
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Gadau Journal of Pure and Allied Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

